CNC turned parts | Horizontal turning technology | Vertical turning technology
Simple and highly complex CNC turned parts manufactured in large and small series
A total portfolio of 17 horizontal and vertical lathes enables us to cover a large bandwidth of machining dimensions and component geometries. From diameter 10 mm to 5,200 mm we offer our services for manufacturing of rotationally-symmetric geometries, flexibly and efficiently. Moreover, several of our lathes have integrated boring and milling units that allow 6-sided complete machining without changing machines. In conjunction with our milling centers and boring mills we are also able to manufacture rotationally-symmetric components with highly-complex prismatic elements. Our grinding technology reliably fulfills increased requirements imposed on dimensional and surface tolerances. Thanks to exclusive use of CNC technology, as well as our in-house programming with preliminary simulations, we manufacture precisely, economically, and with process reliability.
HAVLAT – ACCLAIMED AND CERTIFIED
Commission CNC turned parts from HAVLAT – your advantages at a glance
Installation-ready precision components
Scalable collaboration – from single parts to series
Extensive experience in implementation and consulting
Partial or total CNC processing
Diverse component diameters, 10 to 5,200 mm
Extensive range of materials
Heat treatment and surface treatment in cooperation
Certified quality and energy management
Get a free quote for your CNC turned parts!

This is how job order production works at HAVLAT.
Our CNC turning technology in overview
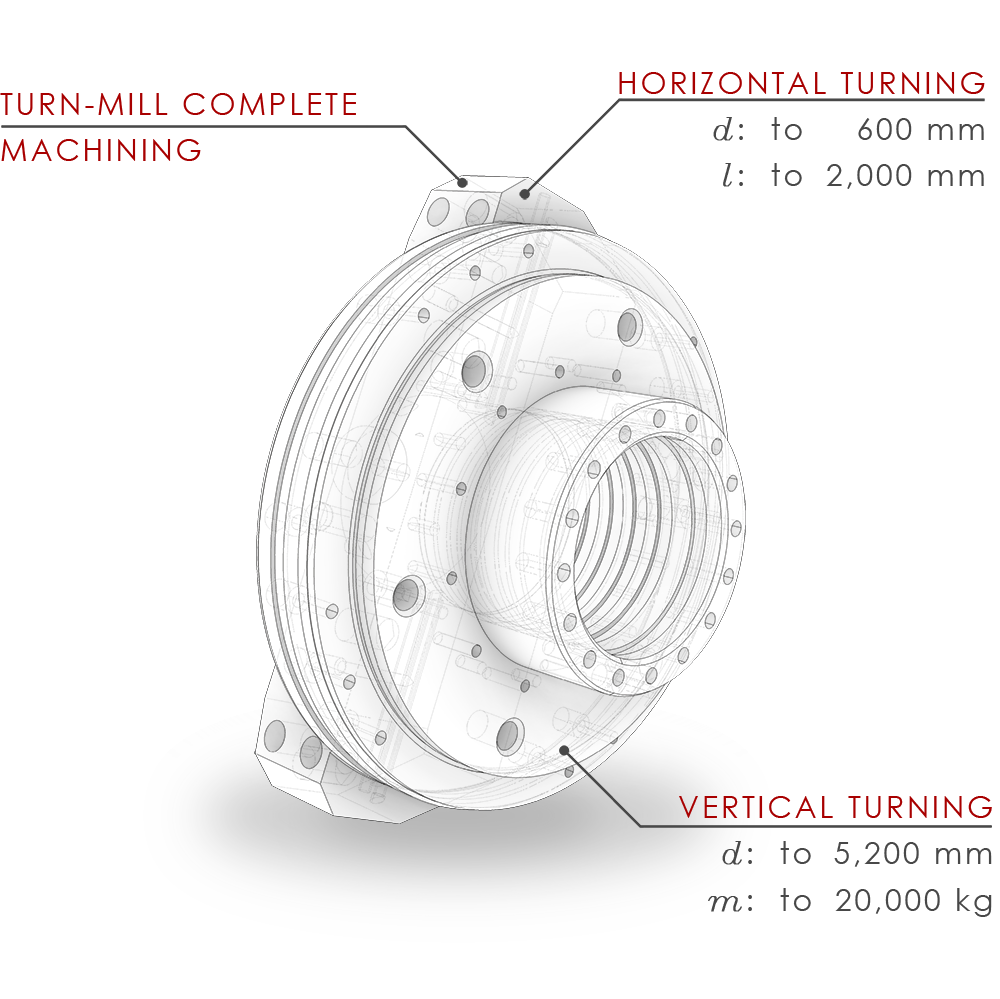
Horizontal Turning Technology
- State-of-the-art CNC turning and milling centers
- Synchronously operating main spindle and counter spindle
- Controlled 5-axis boring and milling unit
- Extensive tool and jig assortment
- Tolerance compliance to 0.01 mm
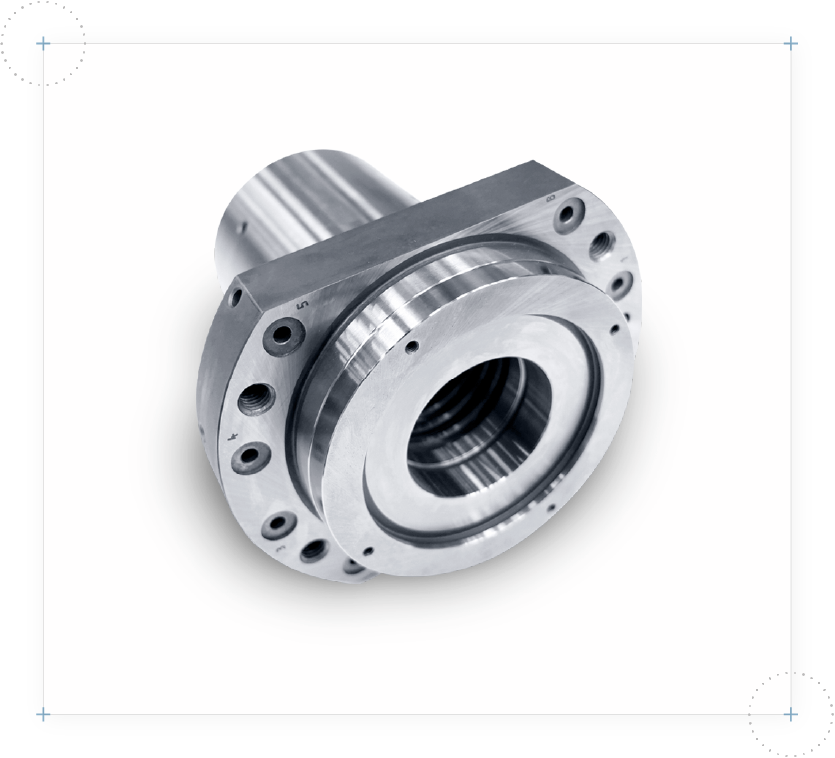

Reference component: Andockflansch
Vertical Turning Technology
- Turning to 5,200 mm (face plate 4,000 mm)
- Maximum component weight 25 t
- Controlled 3-axis boring and milling unit
- Machining of half-components
- Tolerance compliance to 0.02 mm
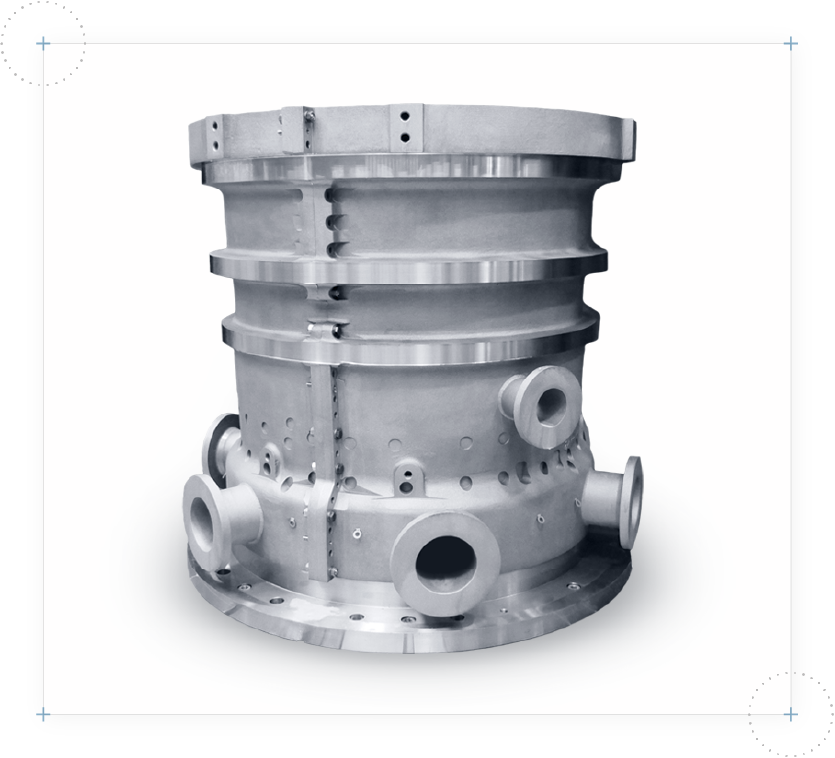

Reference component: Kompressorgehäuse
CNC Turning dimensions
CNC turning machinery at HAVLAT
Our modern, powerful fleet of machines is at your service. Thanks to constant investment in the future, we are assured of our abilities as a CNC job order manufacturer and production service provider in general. We rely on the latest technology from leading machine tool manufacturers and our decades of experience to produce precision components. Why not join us?
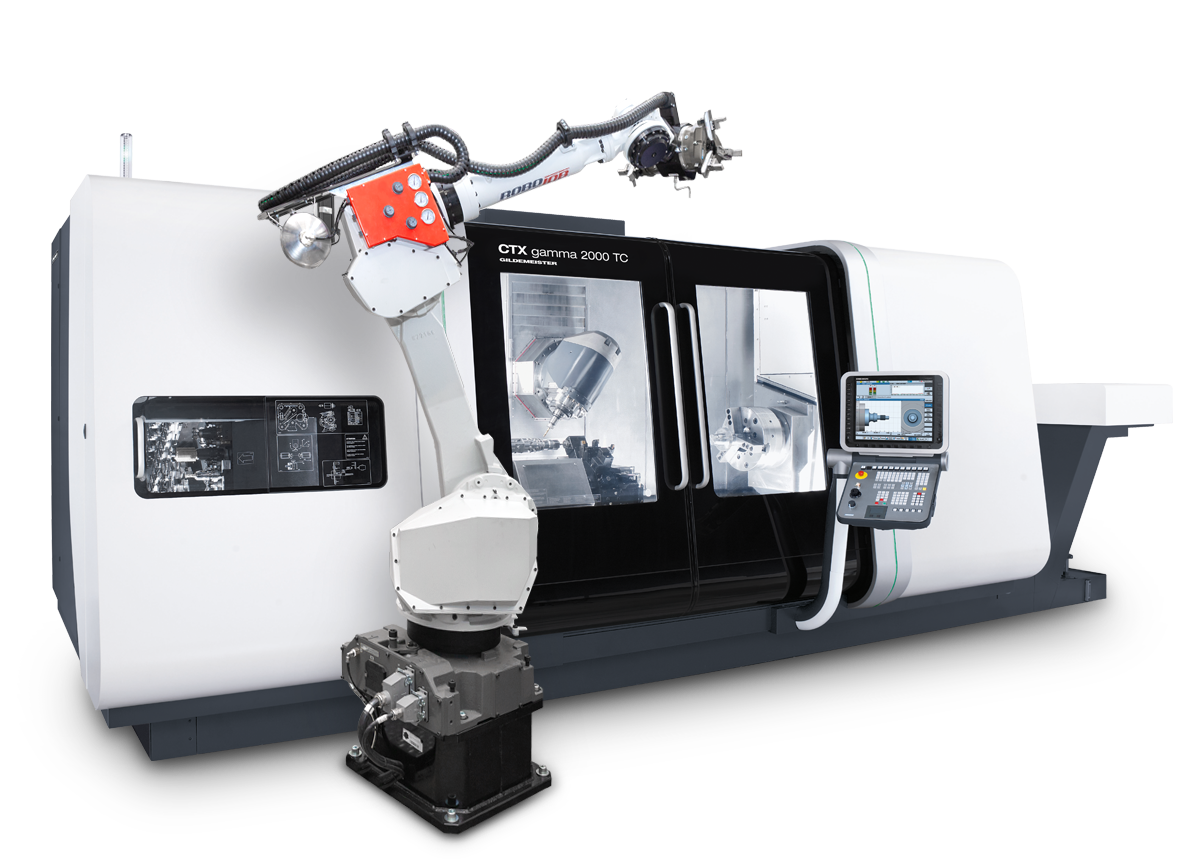

Horizontal lathes
Highlight-Machine :
DMG Mori – CTX gamma 2000 TC
Powerful & process-optimised. Our CTX gamma 2000 TC machines enable a 6-side complete machining for the flexible manufacture of highly complex components. In combination with CNC automatisation, we manufacture your components in any batch size.
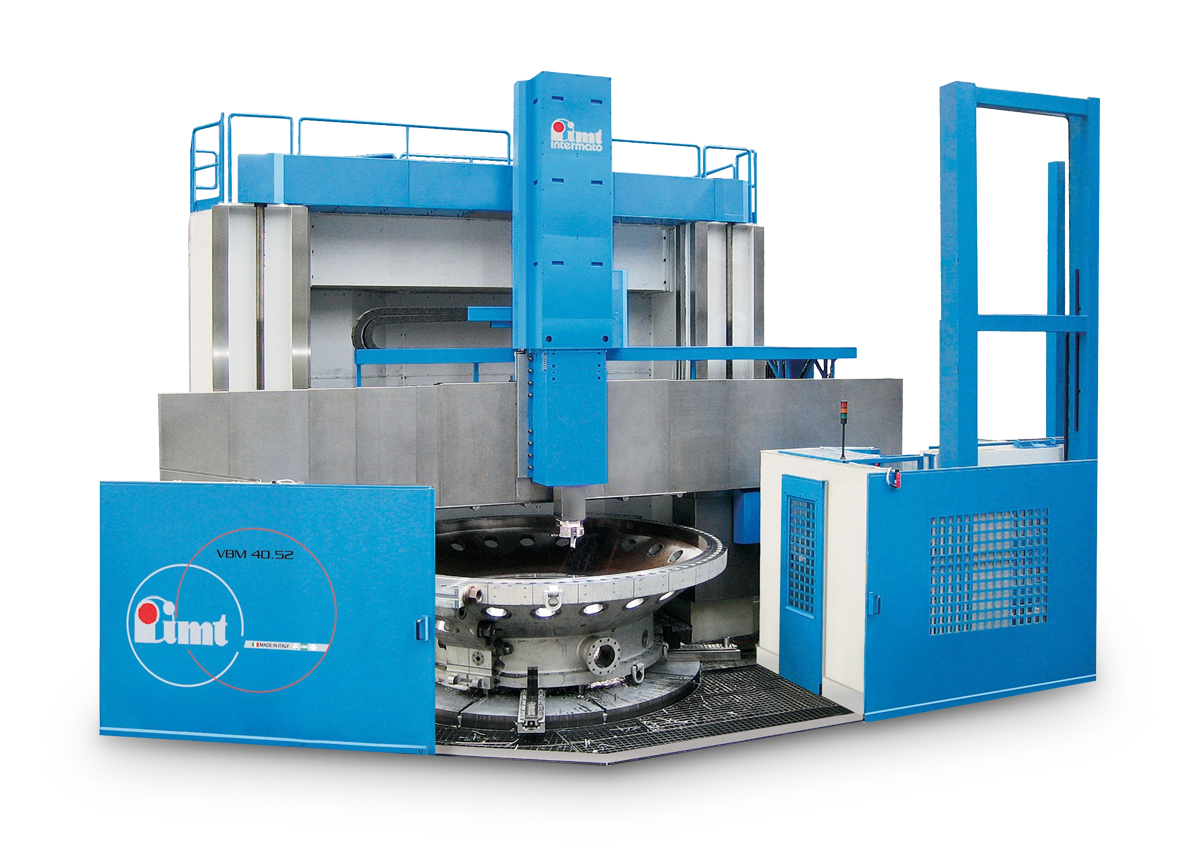

Vertical lathes
Highlight-Machine :
IMT Procast Line – VBM 40/52
Maximized. Turning on the VBM 40/52 is impressive – this is confirmed by workpieces with a diameter of up to 5,200 mm, a height of up to 3,000 mm and a weight of up to 25 t. Through a driven processing spindle, in addition to turning, milling and boring are also possible.

